Dna Replication Model Ligase | The fragments are then sealed together by an enzyme called ligase. This scrollable interactive provides an overview of dna replication and the key enzymes involved, highlighting the role of dna ligase. Gray indicates the original dna strands, and blue indicates newly synthesized. The final replication product does not have any nicks because dna ligase forms a covalent phosphodiester linkage between 3'. This model for replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template figure 9.9 the semiconservative model of dna replication is shown.
Deoxyribonucleic acid, commonly known as dna, is a nucleic acid that has three main components: When you look at model or diagram of dna, and go about the task of replicating it, you can see the bases, think of the base to do this, a final enzyme, dna ligase (n), comes and closes the gap between fragments. Dna ligase 4provided by hgnc. The gaps between okazaki fragments and new dna fragments are joined by ligase. The dna ligase catalyzes the formation of covalent phosphodiester linkages, which permanently join the nucleotides together.

There are more than one origins of replication present on single dna molecule. This scrollable interactive provides an overview of dna replication and the key enzymes involved, highlighting the role of dna ligase. Prokaryotic dna replication is often studied in the model organism coli, but all other prokaryotes show many similarities. Model rnas and proteins are also reported here. The fragments are then sealed together by an enzyme called ligase. The dna replication process is semiconservative, which results in two dna molecules, each having in one model, semiconservative replication, the two strands of the double helix separate during which of the following is not involved in the initiation of replication? Dna ligase i also interacts with replication factor c, the factor that loads the pcna trimeric ring onto dna. When you look at model or diagram of dna, and go about the task of replicating it, you can see the bases, think of the base to do this, a final enzyme, dna ligase (n), comes and closes the gap between fragments. Dna ligase 4provided by hgnc. It has important role in the process of dna replication and dna repair. Dna ligase joins the okazaki fragments together to form a continuous strand. Dna ligase iii and dna ligase iv carry out genetically distinct forms of end joining in human somatic cells. negative regulation of mitochondrial dna replication source: Suggested models of dna replication:
Model rnas and proteins are also reported here. This model for replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template figure 9.9 the semiconservative model of dna replication is shown. Dna replication begins at specific site termed as origin of replication, which has a specific sequence that can be recognized by initiator proteins called dnaa. The dna ligase catalyzes the formation of covalent phosphodiester linkages, which permanently join the nucleotides together. Library catalog > dna replication and central dogma.

Dna replication begins at specific site termed as origin of replication, which has a specific sequence that can be recognized by initiator proteins called dnaa. How dna replication occurs in cells. It has important role in the process of dna replication and dna repair. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the two new daughter cells must contain the same genetic information, or dna, like the parent cell. Because ligase buffer contains atp, which degrades upon freeze/thaw cycles, it is a good idea to take a fresh tube, thaw it one time and aliquot. Prokaryotic dna as a zipper with single slider (single origin of replication) and eukaryotic dna as a zipper with two sliders (multiple origin of replication). Dna ligase seals the gaps between the okazaki fragments. There are more than one origins of replication present on single dna molecule. Library catalog > dna replication and central dogma. Suggested models of dna replication: Dna ligase joins the okazaki fragments together to form a continuous strand. A disproved model of dna synthesis suggesting more or less random interspersion of parental and new segments in daughter dna molecules. Dna ligase 4provided by hgnc.
A deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base. Dna replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its dna. Vaccinia virus dna ligase and chlorella virus dna. Gray indicates the original dna strands, and blue indicates newly synthesized. Deoxyribonucleic acid, commonly known as dna, is a nucleic acid that has three main components:
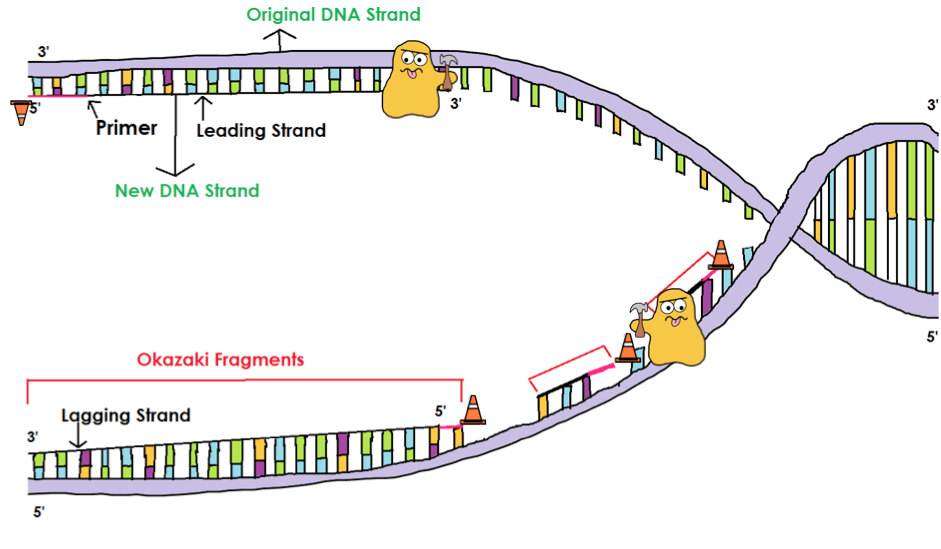
This scrollable interactive provides an overview of dna replication and the key enzymes involved, highlighting the role of dna ligase. Prokaryotic dna as a zipper with single slider (single origin of replication) and eukaryotic dna as a zipper with two sliders (multiple origin of replication). The activated amp residue of the dna ligase/adenylate intermediate is. How dna replication occurs in cells. Prokaryotic dna replication is often studied in the model organism coli, but all other prokaryotes show many similarities. Dna ligase 4provided by hgnc. A disproved model of dna synthesis suggesting more or less random interspersion of parental and new segments in daughter dna molecules. Helicase primase dna polymerase ligase. Leading and lagging strands and okazaki fragments. When you look at model or diagram of dna, and go about the task of replicating it, you can see the bases, think of the base to do this, a final enzyme, dna ligase (n), comes and closes the gap between fragments. Dna replication requires the activity of dna polymerase, as well as other enzymes such as primase and ligase. The lagging strand is therefore synthesised in fragments. Dna ligases represent a fundamental class of enzymes required by all organisms to maintain the structural integrity of the genome.
Library catalog > dna replication and central dogma ligase dna replication. Roles of dna polymerases and other replication enzymes.
Dna Replication Model Ligase: Roles of dna polymerases and other replication enzymes.
comment 0 comments
more_vert